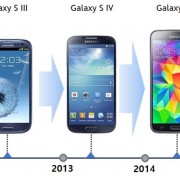
Galaxy S Series Luminance Increase Trend Shows Blue Materials Luminance Needs to be Improved by 3.7 Times

Galaxy S Series`s Blue Materials Luminance Needs to be Improved by 3.7 Times (Source = UBI Research)
Hyunjoo Kang / jjoo@olednet.com
If the Galaxy S Series luminance increase trend continues, it is estimated that the luminance will reach 754 nits within 2-3 years. In order to produce Galaxy S with 754 nits, the luminance of blue emitting materials, that will be used for the product’s AMOLED, is analyzed to require improvement by approx. 3.7 times.
According to AMOLED Characteristics Analysis Report of Galaxy S Series, published by UBI Research, the analysis of luminance increase trend of Galaxy products from S4 released in 2013 shows Galaxy S series with full white luminance of 430 nits and peak white of 754 nits is expected to be produced within 2-3 years. The Galaxy S4 luminance is 338 nits (peak white), and the luminance increased to S7’s 505 nits via S5 and S6’s 400 nits mark. Calculating based on this trend, the future product is analyzed to have 754 nits of luminance.
The report reveals that for Galaxy S7, the luminance of red materials is 142 nits, green 338 nits, and blue 26 nits. To actualize 754 nits screen, the red materials have to improve luminance by approximately 1.5 times, green 1.2 times, and blue 3.7 times. UBI Research explained that for high resolution screen with limited size, emitting materials performance improvement is a must and that technology development should be focused on blue emitting materials.
* Luminance figures (nits) quoted in the article have been measured by UBI Research, with Auto Brightness function switched off. Future luminance forecast is also without this function.