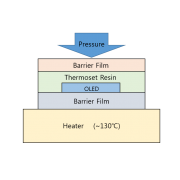
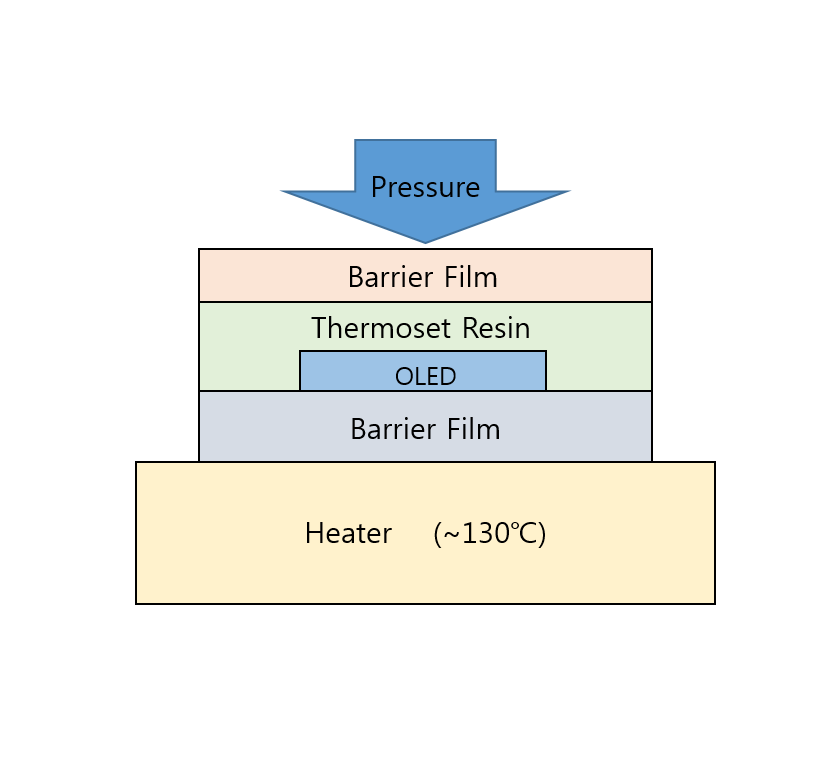
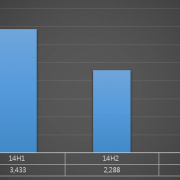
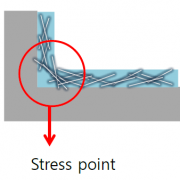
The 3rd section of the 1st OLED Frontier Forum (Jan 28), OLED’s Future, held a panel discussion with government, industry, and academia experts discussing OLED industry development strategy, such as next generation technology development, convergent areas, and personnel training, and future forecast. OLEDNET summarized the answers that each expert gave to the questions of the panel chair (Professor Changhee Lee, Seoul National University).
Jun-hyung Souk (Professor, Sungkyunkwan University)
For SDC mobile, as the OLED depreciation is ending the OLED production cost is becoming almost the same as LCD. If OLED related experts stay within Korean industry as well as the technology, Korea can continue to lead for 4-5 years. In order to achieve the continued leadership, differentiation through flexible R2R has to be carried out, as well as the materials and encapsulation technology development.
Sung-Chul Kim (CTO, SDC)
As a-Si is an existing technology, there is no room for further advancement. Sharp’s difficulty in panel business is due to lack of technology research on the panel. Because one technology can only be used for approximately 7 months, diverse technology development is required.
In-byeong Kang (CTO, LGD)
Fast organizations cannot but win. Therefore, rapid change to OLED from LCD is needed. As difficult is the technology, cooperation between academia and industry is needed. Now is the time when this cooperation for next generation technology development is more in demand. LGD is putting in much effort for OLED profitability.
Sung-Jin Kim (Vice President, Toray Advanced Materials Korea)
Cooperation between materials and manufacturing equipment companies is important in solution process materials development. Particularly, how to control dry process is an important issue. Also, Kim expects the current solution process materials development to show tangible results in 3-5 years.
Junyeob Lee (Professor, Sungkyunkwan University)
Solution process is favorable for materials optimization. From the initial concentration on polymer materials, recently small molecule materials focused soluble materials development is being carried out, and how to implement common layer is an issue. Emitting layer is using the small molecule materials that are being used as evaporation materials. The difference is the higher cost as the solvent is used. Also, as there is an issue (formulation problem) when used in large area, solution is required.
Kyoung-Soo Kim (Vice President, Korea Display Industry Association)
Expert acquirement is a key issue. Through upgraded cooperation between industry and academia, and industries, cooperation between panel, manufacturing equipment, and materials has to progress into a positive cycle. Also the open platform regarding new OLED application is needed.
Young-Ho Park (PD, Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology)
Flexible display competitiveness acquirement is a big concern. Programs for challenging R&D, and high added value product/technology development, and R&D infra establishment (highly cost-effective R&D) have to be considered.