During the International Advanced Materials & Application Technology Expo (November 25-27), Professor Jang-Ung Park of Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) gave an in-depth lecture on transparent electrode’s new technology and research results under the presentation title of ‘Technology Trend and Development Direction of High Performance Transparent & Stretchable Electrodes Using Graphene and Ag Nanowire Complex’.
Transparent electrode is an electronic component with usually ≥80% transparency, and sheet tension of ≤500Ω/ㅁ of conductivity. This technology is widely used in electronics including LCD front electrode and OLED electrode in display, touchscreen, solar cell, and optoelectronic device.
Park explained that the main market for transparent electrode is display and touchscreen, and announced that the transparent electrode market is to grow into US$4,800 million in 2020 from 2015’s US$ 3,400 million.
The electrode materials that is mainly being used at present is ITO (indium tin oxide) film produced through evaporation or sputtering. ITO’s merits include good conductivity from the low sheet tension and suitable for mass production. However, China is the main producer of the rare main material, indium, and has a drawback of high processing temperature. As such, research for indium replacement is continuing.
Graphene, CNT (carbon nano tube), Ag nanowire, and metal mesh are some of the materials that are in the spotlight as ITO replacement. However, Park emphasized that transparent electrodes that are being developed at present have difficulty in surpassing ITO in terms of electronical and optical properties. Instead, he explained that as the display shape changes, the replacement material can be used for displays where ITO cannot be applied.
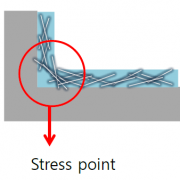
At present, ITO is being used as the main electrode material for flat display. However, its weakness against mechanical stress and limitation in flexibility led to some views that flexible display application will be difficult. Regarding this Park explained that thickness of substrate is more important than ITO’s traits for display’s curvature radius and therefore if substrate becomes thinner, ITO can be applied even to foldable display as well as flexible. He added that although folding the display is acceptable, stretchable display is impossible as the properties are destroyed when pulled.
Park emphasized that in order for the wearable display market, including the smartwatch market, to grow, the comfort of the user is important. He reported as a human body does not conform to a specific curvature radius, to improve the user comfort, stretchable panel that can bend in diverse directions is a necessity. For this to be possible, transparent electrode that can replace ITO is required.
For example, watch shaped application can be replaced with stretchable display up to the strap part that wraps around the wrist. Glasses shaped application can have stretchable display for curved areas such as lenses. Also, within textiles industry, research into smart textiles through electronic circuit application is continuing.
As the transparent electrode that can replace ITO, Park suggested graphene and Ag nanowire complex. Ag nanowire reduces high sheet tension of graphene, and graphene prevents Ag nanowire’s oxidization, complementing each other. Park revealed that ≥90% transmittance and ≤30Ω/ㅁ was achieved through research. He emphasized as stretchability increased to 100%, it is suitable for stretchable display.
According to Park, transparent electrode can be applied to transparent stretchable sensor and transparent TFT as well as display. With confirmation of continued research regarding this issue, Park concluded his presentation.





 3月8日から9月の二日間、UBIリサーチが開催した第3回OLED Korea Conferenceで、中国Visionox Li Lin首席研究員は『Development of Foldable AMOLED Display』をテーマに講演を行った。
3月8日から9月の二日間、UBIリサーチが開催した第3回OLED Korea Conferenceで、中国Visionox Li Lin首席研究員は『Development of Foldable AMOLED Display』をテーマに講演を行った。